Sensational Info About How To Check Umask

In binary all octets represent the following for the.
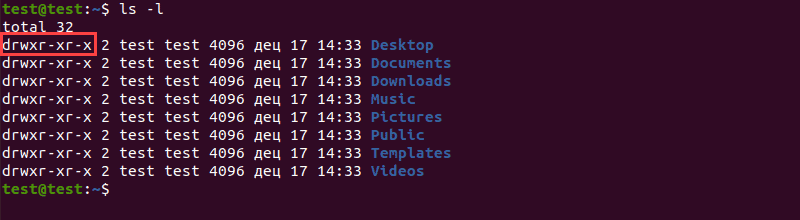
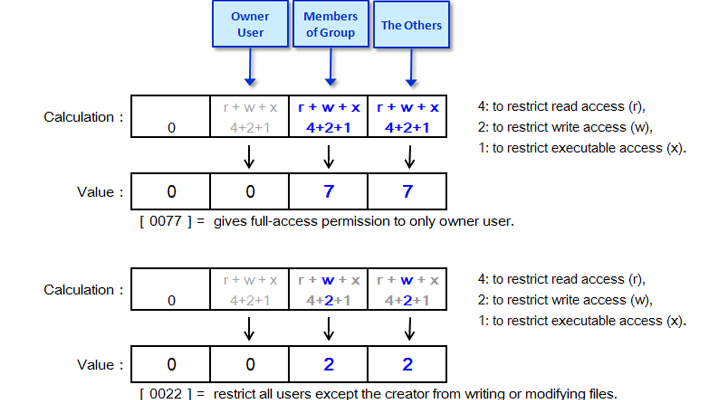
How to check umask. To determine the umask value you want to set, subtract the value of the permissions you want from 666 (for a file) or 777 (for a directory). That’s a default, as you can see, looking from the left, the user that has created the file (root for me) can read and write the file, the group (root) can only read it and all the others can read the. The remainder is the value to use with the umask.
The remainder is the value to use with the umask. Running the umask command by itself provide the default permissions that are assigned when a file or folder is. Permission octets mean the following.
The desired umask value represented in numeric. Then, create a new login shell to become the new user: From a terminal session, enter the following command:
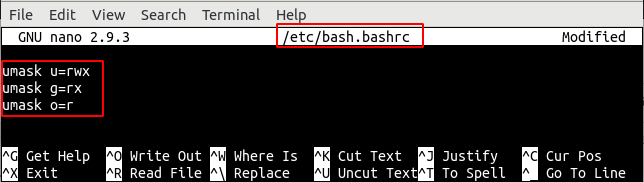
Here, the first digit, 0 is called the sticky bit, it is a special security feature. To calculate the umask value, simply subtract the desired permissions from the default one: In this method, umask will changed only when the session is active.
First you need to check the current umask values by running umask command as shown below. To view your system's current umask value, enter the command: To determine the umask value you want to set, subtract the value of the permissions you want from 666 (for a file) or 777 (for a directory).
To view the current umask value, we use the umask command. If you want to check default umask value in linux system just type “umask” command. The screen displays the following values: